Julia 可视化库:VegaLite.jl 【笔记4 - 数据来源】
内部数据来源
Julia 表格数据结构
VegaLite.jl 涵盖了 julia 生态系统中的大多数表格数据结构: DataFrames.jl,JuliaDB.jl,IndexedTables.jl,各种文件IO库(CSVFiles.jl,FeatherFiles.jl,ExcelFiles.jl,StatFiles.jl,ParquetFiles.jl)以及 Query.jl 中的表格形式。
管道操作数据
using VegaLite, VegaDatasets, Query
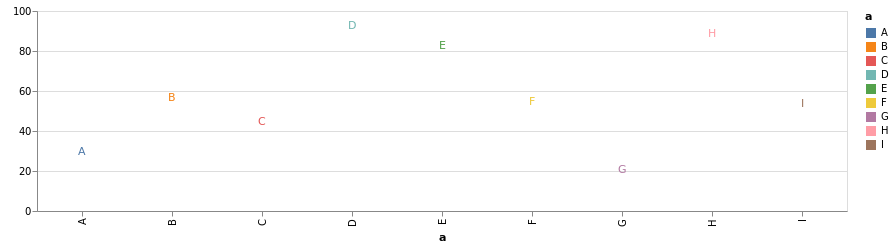
cars = dataset("cars");
cars |>
@vlplot(
:point,
x=:Horsepower,
y=:Miles_per_Gallon
)
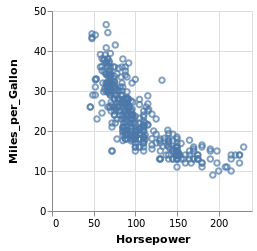
上面的写法等价于 @vlplot(:point, data=cars, x=“Horsepower:q”, y=“Miles_per_Gallon:q”)
cars |> # 绘制日本地区的情况
@filter(_.Origin=="Japan") |>
@vlplot(
:point,
x={:Horsepower, scale={zero=false}},
y=:Miles_per_Gallon)
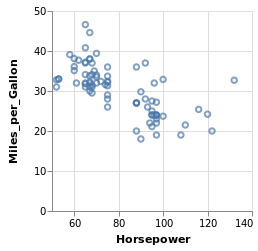
# 上面的写法等价于
cars |>
@vlplot(
:point,
transform=[{filter="datum.Origin == 'Japan'"}],
x={:Horsepower, scale={zero=false}},
y=:Miles_per_Gallon)

外部数据来源
主要是从 本地文件路径 和 网络 获得数据。这一部分功能目前还不完善。
参见:http://fredo-dedup.github.io/VegaLite.jl/stable/userguide/data.html#Referencing-external-data-1
using FilePaths
# path = p"folder/filename.csv";
# path |> @vlplot(:point, x=:a, y=:b)
上面的命令运行报错,估计功能还没实现。推荐将数据读取进来,然后进行管道操作 ↓
using CSV
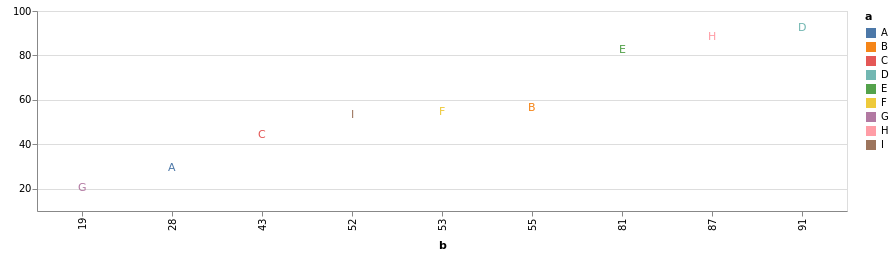
data = CSV.read("data/data.csv") # 笔记 3 中的数据
| a | b | |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | A | 28 |
| 2 | B | 55 |
| 3 | C | 43 |
| 4 | D | 91 |
| 5 | E | 81 |
| 6 | F | 53 |
| 7 | G | 19 |
| 8 | H | 87 |
| 9 | I | 52 |
data |> @vlplot(:text, x={:a, scale={zers=false}}, y={:b, title=nothing}, text=:a, color=:a)
data |> @vlplot(:text, x="b:o", y={:b, title=nothing, scale={zero=false}}, text=:a, color=:a)
Julia 可视化库:VegaLite.jl 【笔记5 - 绘图类型 mark】
Galary & API
VegaLite.jl 文档绘图例子: http://fredo-dedup.github.io/VegaLite.jl/stable/index.html
VegaLite 官方 Example Galary: Example Gallery | Vega-Lite
VegaLite API 文档( JSON 格式): Overview | Vega-Lite
mark 特性
// Json 版本
{
...
"mark": {
"type": ..., // mark
...
},
...
}
# Julia 版本
@vlplot(
mark={
typ=:..., # 注意不能使用 Julia 预留关键字 type
...
}
)
狭义的 mark 指的是 mark 键下的 type 字段
| 类型 | mark → type | x | y | color | shape | size |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 线图 | :line | |||||
| 轨迹图 | :trace | |||||
| 垂线、水平线图 | :rule | |||||
| 空心散点图 | :point | |||||
| 圆形实心散点图 | :circle | |||||
| 方形实心散点图 | :square | |||||
| 文字标注图 | :text | text=:var | ||||
| 柱状图 | :bar | |||||
| 直方图 | :bar | x={:a, bin=true} | y=“count()” | |||
| 热力图、填充图 | :rect | x=“x:o” | y=“y:o” | color=:z | ||
| area plot (面积堆积图) | :area | |||||
| strip plot(分布散点图) | :tick | x=:x | y=“y:o” | |||
| 地理图 | :geoshape |
广义的 mark 包括:type、 style、 clip 三部分。
详细 mark 特性参看: Mark | Vega-Lite
几个栗子
运行例子代码前需要加载以下库 ↓
using VegaLite, VegaDatasets
Example1
dataset("stocks") |>
@vlplot(
:trail, # 等价于 mark = :trail 等价于 mark={typ=:trail}
x={
"date:t",
axis={format="%Y"}
},
y=:price,
size=:price,
color=:symbol
)
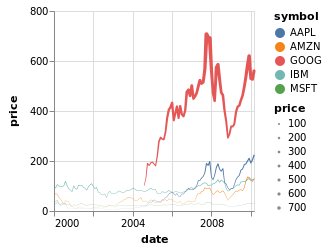
Example2
dataset("unemployment-across-industries") |>
@vlplot(
:area, # 等价于 mark = :area 等价于 mark={typ=:area}
width=300, height=200,
x={
"yearmonth(date)",
axis={
domain=false,
format="%Y",
tickSize=0
}
},
y={
"sum(count)",
axis=nothing,
stack=:center
},
color={
:series,
scale={scheme="category20b"}
}
)
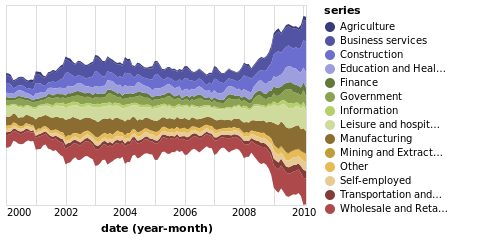
Example3
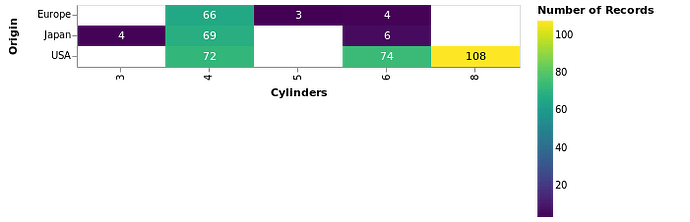
cars |>
@vlplot(
y="Origin:o",
x="Cylinders:o",
config={
scale={bandPaddingInner=0, bandPaddingOuter=0},
text={baseline=:middle}
}
) +
@vlplot(
:rect, # 等价于 mark = :rect 等价于 mark={typ=:rect}
color="count()") +
@vlplot(
:text, # 等价于 mark = :text 等价于 mark={typ=:text}
text="count()",
color={
condition={
test="datum['count_*'] > 100",
value=:black
},
value=:white
}
)
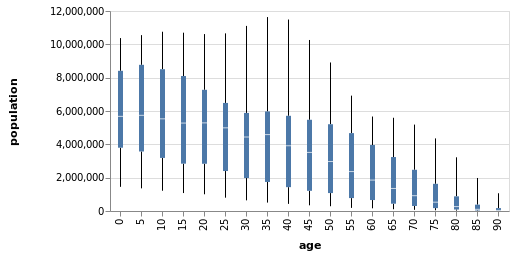
Example4
dataset("population") |>
@vlplot(
transform=[{
aggregate=[
{op=:q1, field=:people, as=:lowerBox},
{op=:q3, field=:people, as=:upperBox},
{op=:median, field=:people, as=:midBox},
{op=:min, field=:people, as=:lowerWhisker},
{op=:max, field=:people, as=:upperWhisker}
],
groupby=[:age]
}]
) +
@vlplot(
mark={:rule, style=:boxWhisker},
y={"lowerWhisker:q", axis={title="population"}},
y2="lowerBox:q",
x="age:o"
) +
@vlplot(
mark={:rule, style=:boxWhisker},
y="upperBox:q",
y2="upperWhisker:q",
x="age:o"
) +
@vlplot(
mark={:bar, style=:box},
y="lowerBox:q",
y2="upperBox:q",
x="age:o",
size={value=5}
) +
@vlplot(
mark={:tick, style=:boxMid},
y="midBox:q",
x="age:o",
color={value=:white},
size={value=5}
)
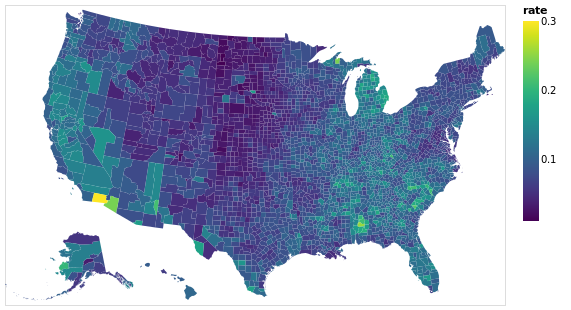
Example5
us10m = dataset("us-10m").path
unemployment = dataset("unemployment.tsv").path
p = @vlplot(
:geoshape, # mark
width=500, height=300,
data={
url=us10m,
format={
typ=:topojson,
feature=:counties
}
},
transform=[{
lookup=:id,
from={
data=unemployment,
key=:id,
fields=["rate"]
}
}],
projection={
typ=:albersUsa
},
color="rate:q"
)
Julia 可视化库:VegaLite.jl 【笔记6 - transform 之 aggregate】
aggregate 特性
// Json 版本
{
...
"transform": [
{
// Aggregate Transform
"aggregate": [
{"op": ..., "field": ..., "as": ...},
{"op": ..., "field": ..., "as": ...},
...],
"groupby": [...]
}
...
],
...
}
# Julia 版本
@vlplot(
...
transform=[{
aggregate=[
{op=..., field=..., as=...},
{op=..., field=..., as=...},
...],
groupby=[...]
},
...
],
...
)
-
aggregate字段下有op、field、as三个必需的属性。-
field指的是操作的变量对象。 -
as给操作后的变量一个名称,该名称于所在的代码环境内起作用。 -
op支持以下操作函数。在Json格式中函数名称使用双引号,即使用"op": "operation",在Julia中语法为op=:operation。
-
-
aggregate可与groupby字段连用,实现对不同的组进行操作。
| operation | 解释 | operation | 解释 |
|---|---|---|---|
| count | 计数 | stderr | 标准误 |
| valid | 对非空等数值计数 | median | 中位数 |
| missing | 空值或未定义字段值 | q1 | 下四分位数 |
| distinct | 对不同字段的值计数 | q3 | 上四分位数 |
| sum | 求和 | ci0 | 根据bootstrapped方法得到的95%下置信区间 |
| mean | 均值 | ci1 | 根据bootstrapped方法得到的95%上置信区间 |
| average | 均值 | min | 最小值 |
| variance | 样本方差 | max | 最大值 |
| variancep | 总体方差 | argmin | 达到最小值的数据对象 |
| stdev | 样本标准差 | argmax | 达到最大值的数据对象 |
| stdevp | 总体标准差 |
栗子
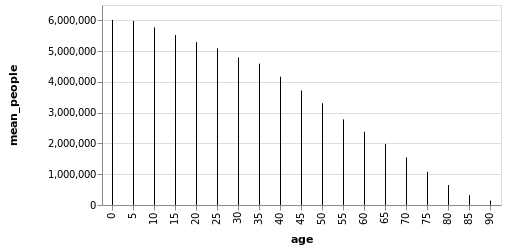
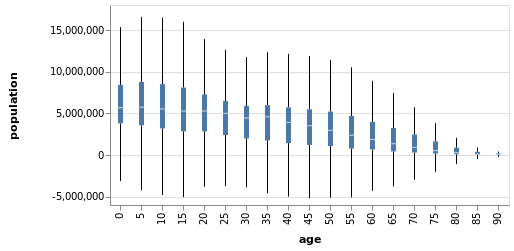
一个简单的例子:画出 poplulation 数据集中 150 年各年龄段的平均人口数量。
using VegaLite, VegaDatasets, DataFrames
popu = DataFrame(dataset("population"))
describe(popu[:,1]) # 1850-2000 年 -> 151 年
dataset("population") |>
@vlplot(
transform=[
{
aggregate=[
{op=:mean, field=:people, as=:mean_people} # 每个年龄段的人口均值
],
groupby=[:age] # 以年龄段分组
}
],
:rule,
x="age:o",
y="mean_people:q",
)
Summary Stats:
Mean: 1927.333333
Minimum: 1850.000000
1st Quartile: 1880.000000
Median: 1930.000000
3rd Quartile: 1970.000000
Maximum: 2000.000000
Length: 570
Type: Int64
应用
一个带有最大值、最小值触须的箱线图 ↓
using VegaLite, VegaDatasets
dataset("population") |>
@vlplot(
transform=[{
aggregate=[
{op=:q1, field=:people, as=:lowerBox},
{op=:q3, field=:people, as=:upperBox},
{op=:median, field=:people, as=:midBox},
{op=:min, field=:people, as=:lowerWhisker},
{op=:max, field=:people, as=:upperWhisker}
],
groupby=[:age]
}]
) +
@vlplot(
mark={:rule, style=:boxWhisker},
y={"lowerWhisker:q", axis={title="population"}},
y2="lowerBox:q",
x="age:o"
) +
@vlplot(
mark={:rule, style=:boxWhisker},
y="upperBox:q",
y2="upperWhisker:q",
x="age:o"
) +
@vlplot(
mark={:bar, style=:box},
y="lowerBox:q",
y2="upperBox:q",
x="age:o",
size={value=5}
) +
@vlplot(
mark={:tick, style=:boxMid},
y="midBox:q",
x="age:o",
color={value=:white},
size={value=5}
)

Julia 可视化库:VegaLite.jl 【笔记7 - transform 之 calculate】
calculate 特性
// Json 版本
{
...
"transform": [
// Calculate Transform
{"calculate": ..., "as" ...},
{"calculate": ..., "as" ...},
{"filter": ...},
...
],
...
}
# Julia 版本
@vlplot(
...
transform=[
{calculate= ..., as= ...},
{calculate= ..., as= ...},
{filter= ...},
...
],
...
)
-
calculate的值为expression表达式,datum表示当前输入的数据对象,datum.a表示对输入数据列名为 a 的数据进行计算。 -
expression中默认的常量有: NaN、 E (常数 e )、LN2 ($log_e 2$)、LN10 ($log_e 10$)、LOG2E ($log_2 e$)、LOG10E ($log_{10} e$)、MAX_VALUE (可表示的最大正数)、MIN_VALUE (可表示的最小正数)、PI ($\pi$)、SQRT1_2($\sqrt {1/2})、*SQRT2* (\sqrt 2$)等。 -
calculate可与filter连用,对满足某些条件的数据进行计算操作。
栗子
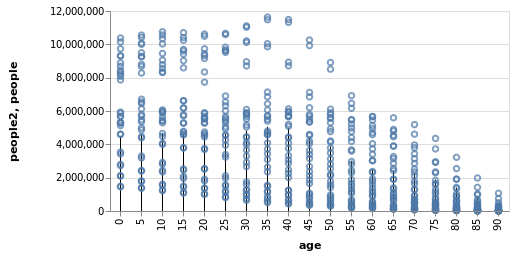
使用 LOG10E 常量,以历史上各年龄段人口数量顶峰值与这个常量的乘积作为y轴,作出垂直线图。并将各年龄段的历史人口数情况以散点形式添加到图上。
using VegaLite, VegaDatasets
dataset("population") |>
@vlplot() + # 这里相当于定义一层 layer,"+" 表示添加图层
@vlplot(
transform=[
{
calculate="LOG10E * datum.people",
# 相当于 log(10, e) * max(people), log(10, e) ≈ 0.434
as=:people2
}
],
:rule,
x="age:o",
y="people2:q",
)+
@vlplot(
:point,
x="age:o",
y="people:q"
)
应用
带有 1.5 倍四分位距的箱线图 ↓
using VegaLite, VegaDatasets
dataset("population") |>
@vlplot(
transform=[
{
aggregate=[
{op=:q1, field=:people, as=:lowerBox},
{op=:q3, field=:people, as=:upperBox},
{op=:median, field=:people, as=:midBox}
],
groupby=[:age]
},
{
calculate="datum.upperBox - datum.lowerBox",
as=:IQR
},
{
calculate="datum.lowerBox - datum.IQR * 1.5",
as=:lowerWhisker
},
{
calculate="datum.upperBox + datum.IQR * 1.5",
as=:upperWhisker
}
]
) +
@vlplot(
mark={:rule, style=:boxWhisker},
y={"lowerWhisker:q", axis={title="population"}},
y2="lowerBox:q",
x="age:o"
) +
@vlplot(
mark={:rule, style=:boxWhisker},
y="upperBox:q",
y2="upperWhisker:q",
x="age:o"
) +
@vlplot(
mark={:bar, style=:box},
y="lowerBox:q",
y2="upperBox:q",
x="age:o",
size={value=5}
) +
@vlplot(
mark={:tick, style=:boxMid},
y="midBox:q",
x="age:o",
color={value=:white},
size={value=5}
)
Julia 可视化库:VegaLite.jl 【笔记8 - transform 之 filter】
filter 特性
// Json 版本
{
...
"transform": [
// Filter Transform
{"filter": ...}
...
],
...
}
# Julia 版本
@vlplot(
...
transform=[
{filter= ...},
...
],
...
)
filter 的值为逻辑值有以下四种情况:
-
表达式字符串,以
datum标示当前输入数据对象。如filter="datum.a > 60"表示筛选出数据中字段为 a ,其值大于 60 的整个数据对象。 -
包含以下字段谓语: equal (等于), lt (小于), lte (小于等于), gt (大于), gte (大于等于), range (表示数值或者时间范围), oneOf (表示属于某个集合)。
如 filter={field=:car_color, equal=“red”}} 表示筛选 car_color 为 red 的数据对象; filter={field=:car_color, oneOf=[“red”, “yellow”]}} 表示筛选 car_color 为 red 或者 yellow 的数据对象。
-
selection predicate。参见: Filter Transform | Vega-Lite
-
前三种情况的组合。
栗子
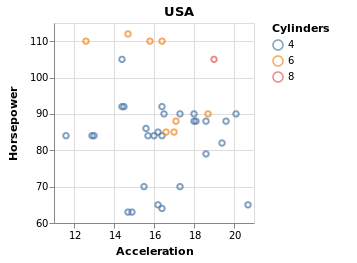
画出 cars 数据集中,1980年至1982年美国地区的汽车情况。
using VegaLite, VegaDatasets
dataset("cars") |>
@vlplot(
transform=[
{filter="datum.Origin=='USA'"}, # 注意字符串内层使用的单引号
{filter={field=:Year, oneOf=["1980-01-01", "1981-01-01", "1982-01-01"]}},
],
:point,
x={:Acceleration, scale={zero=false}}, # 坐标范围不从 0 开始
y={:Horsepower, scale={zero=false}},
color="Cylinders:n",
title="USA"
)
应用
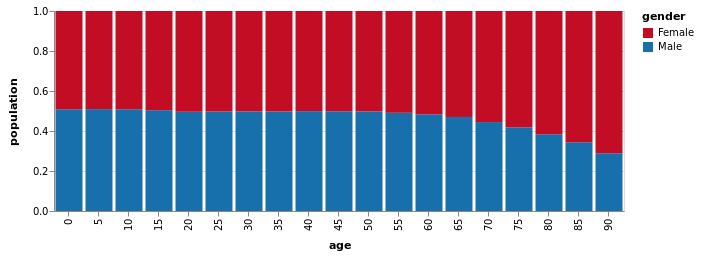
描绘20世纪世界人口各年龄段性别比例构成情况。
using VegaLite, VegaDatasets
dataset("population") |>
@vlplot(
:bar,
transform=[
{filter={field=:year, range=[1900, 2000]}},
{calculate="datum.sex==2 ? 'Female' : 'Male'",as="gender"}
],
enc={
y={
"sum(people)",
axis={title="population"},
stack=:normalize # 归一化
},
x={
"age:o",
scale={rangeStep=30} # 调整柱子的宽度
},
color={
"gender:n",
scale={range=["#c30d24", "#1770ab"]}
}
}
)
完 ![]()