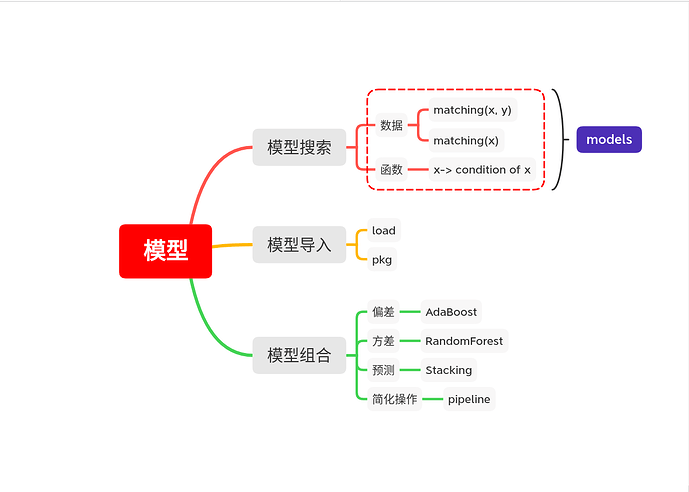
1. 模型搜索
1.1 用数据搜索
以波士顿房价数据集为例,寻找适合的模型
X, y = @load_boston
models(matching(X, y))
不过在此之前我们先看看数据集的科学类型
schema(X)
| _.name | _.types | _.scitypes |
|---|---|---|
| Crim | Float64 | Continuous |
| Zn | Float64 | Continuous |
| Indus | Float64 | Continuous |
| NOx | Float64 | Continuous |
| Rm | Float64 | Continuous |
| Age | Float64 | Continuous |
| Dis | Float64 | Continuous |
| Rad | Float64 | Continuous |
| Tax | Float64 | Continuous |
| PTRatio | Float64 | Continuous |
| Black | Float64 | Continuous |
| LStat | Float64 | Continuous |
scitype(y)
AbstractArray{Continuous, 1}
julia> models(matching(X, y))
(name = ARDRegressor, package_name = ScikitLearn, ... )
(name = AdaBoostRegressor, package_name = ScikitLearn, ... )
(name = BaggingRegressor, package_name = ScikitLearn, ... )
(name = BayesianRidgeRegressor, package_name = ScikitLearn, ... )
(name = ConstantRegressor, package_name = MLJModels, ... )
...
1.2 用函数搜索
我们先用搜索到的模型来举例
info("ARDRegressor", pkg="ScikitLearn")
julia> info("ARDRegressor", pkg="ScikitLearn")
Bayesian ARD regression.
→ based on [ScikitLearn](https://github.com/cstjean/ScikitLearn.jl).
→ do `@load ARDRegressor pkg="ScikitLearn"` to use the model.
→ do `?ARDRegressor` for documentation.
(name = "ARDRegressor",
package_name = "ScikitLearn",
is_supervised = true,
docstring = "Bayesian ARD regression.\n→ based on [ScikitLearn](https://github.com/cstjean/ScikitLearn.jl).\n→ do `@load ARDRegressor pkg=\"ScikitLearn\"` to use the model.\n→ do `?ARDRegressor` for documentation.",
hyperparameter_ranges = (nothing, nothing, nothing, nothing, nothing, nothing, nothing, nothing, nothing, nothing, nothing, nothing),
hyperparameter_types = ("Int64", "Float64", "Float64", "Float64", "Float64", "Float64", "Bool", "Float64", "Bool", "Bool", "Bool", "Bool"),
hyperparameters = (:n_iter, :tol, :alpha_1, :alpha_2, :lambda_1, :lambda_2, :compute_score, :threshold_lambda, :fit_intercept, :normalize, :copy_X, :verbose),
implemented_methods = [:clean!, :fit, :fitted_params, :predict],
is_pure_julia = false,
is_wrapper = true,
load_path = "MLJScikitLearnInterface.ARDRegressor",
package_license = "BSD",
package_url = "https://github.com/cstjean/ScikitLearn.jl",
package_uuid = "3646fa90-6ef7-5e7e-9f22-8aca16db6324",
prediction_type = :deterministic,
supports_online = false,
supports_weights = false,
input_scitype = Table{_s23} where _s23<:(AbstractArray{_s25,1} where _s25<:Continuous),
target_scitype = AbstractArray{Continuous,1},
output_scitype = Unknown,)
这里我们用函数指定模型的输入数据的类型与输出数据的类型来寻找模型
fn(x) = x.input_scitype <: Table{T1} where T1 <: (AbstractArray{T2,1} where T2 <: Continuous)
models(fn)
(name = ARDRegressor, package_name = ScikitLearn, ... )
(name = AdaBoostClassifier, package_name = ScikitLearn, ... )
(name = AdaBoostRegressor, package_name = ScikitLearn, ... )
(name = AffinityPropagation, package_name = ScikitLearn, ... )
(name = AgglomerativeClustering, package_name = ScikitLearn, ... )
(name = BaggingClassifier, package_name = ScikitLearn, ... )
2. 查看模型信息
紧接上面的查询到的内容info("ARDRegressor", pkg="ScikitLearn")
输入的X为
input_scitype = Table{_s23} where _s23<:(AbstractArray{_s25,1} where _s25<:Continuous),
得到的y的科学类型为
target_scitype = AbstractArray{Continuous,1},
3. 加载模型
按照文档里的加载模型,随便试一下好了
→ do
@load ARDRegressor pkg="ScikitLearn"to use the model.
→ do?ARDRegressorfor documentation.
为什么导入的方式这么奇怪,不用原生的import呢?
这是因为MLJ是一个界面,他负责把一堆模型的用法统一成一个样子,但是他内置的模型比较少,需要从其他语言中调用模型,所以用@load从外面把模型引入,由于有许多机器学习包的模型名字是一样的,需要指定包的名称,在@load后面指定pkg。
如果不知道pkg的话,那么提供模型的包必须是唯一的
@load ARDRegressor pkg=ScikitLearn
model = ARDRegressor()
mach = fit!(machine(model, X, y))
评估一下吧
evaluate!(mach, resampling = CV(nfolds = 6, shuffle = true, rng = StableRNG(444)),
measure = [rms, l1, l2])
| _.measure | _.measurement | _.per_fold |
|---|---|---|
| rms | 5.01 | [4.3, 5.85, 5.04, 5.19, 4.06, 5.41] |
| l1 | 3.5 | [3.19, 3.97, 3.58, 3.66, 2.89, 3.7] |
| l2 | 25.1 | [18.5, 34.2, 25.4, 26.9, 16.5, 29.2] |
| _.per_observation = [missing, [[4.84, 1.0, …, 7.41], [3.67, 0.981, …, 7.29], [4.91, 5.23, …, 3.21], [2.76, 2.83, …, 3.67], [2.63, 0.412, …, 0.468], [0.18, 0.043, …, 1.02]], [[23.4, 1.0, …, 54.9], [13.5, 0.962, …, 53.2], [24.1, 27.4, …, 10.3], [7.64, 8.03, …, 13.5], [6.94, 0.17, …, 0.219], [0.0325, 0.00185, …, 1.05]]] |
还不错,哟系
3. 组合模型
3.1 减小偏差 AdaBoost
MLJ的资料里找不到这个,但是我发现在MLJ中可以搜索到AdaBoost模型,RandomForest也是一样的
3.2 减小方差 RandomForest
虽然MLJ中提供了RandomForest的模型,但是我们可以用EnsembleModel自己造一个
X, y = @load_boston
@load DecisionTreeRegressor
forest_model = EnsembleModel(atom = DecisionTreeRegressor(), n = 100) # atom 为分类器, n为分类器的个数
random_forest = machine(forest_model, X, y)
3.3 提升预测 Stacking
文档里只找到关于学习网络的Stacking策略,好像对普通模型没有讲,我等会再去问问吧
3.4 简化操作 pipeline
pipeline为我们提供了一条龙服务,就像流水线一样从数据准备到数据分析一步到位
先让我们看看需要经过多次处理的例子
using MLJ
using MLJModels # for transform
X = (age = [23, 45, 34, 25, 67],
gender = categorical(['m', 'm', 'f', 'm', 'f']))
height = [67.0, 81.5, 55.6, 90.0, 61.1]
@load KNNRegressor pkg=NearestNeighbors
X1 = coerce(X, :age => Continuous)
# OneHotEncoder
model1 = OneHotEncoder()
mach1 = fit!(machine(model1, X1))
X2 = transform(mach1, X1)
# KNNRegressor 拟合
model2 = KNNRegressor(K = 2)
# 最后评估
evaluate(model2, X, height, resampling = Holdout(), measure = l2)
再来看看用pipeline的例子
pipe = @pipeline(X-> coerce(X, :age => Continuous),
OneHotEncoder,
KNNRegressor(K=2))p
evaluate(pipe, X, height, resampling = Holdout(), measure = l2)
我们可以往@pipeline宏里传递函数或model
如果要修改pipeline对象中的组成部分的参数,可以直接这样
pipe.knn_regressor.K = 2
3.5 一些疑问
pipeline的一些关键字参数我有些不懂,尤其是target
target=… - any Unsupervised model or Function
inverse=… - any Function (unspecified if target is Unsupervised)
invert_last - set to true to delay target inversion to end of pipeline (default=true)
prediction_type - prediction type of the pipeline; possible values: :deterministic, :probabilistic, :interval (default=:deterministic if not inferable)
operation - operation applied to the supervised component model, when present; possible values: predict, predict_mean, predict_median, predict_mode (default=predict)
name - new composite model type name; can be any name not already in current global namespace (autogenerated by default)
文档在这里,有兴趣帮我看看吧![]()
补充
像模型搜索一样,评估模型时的指标也可以搜索
y = [1,2,3]
scitype(y) # AbstractArray{Count,1}
measure(matching(y))
julia> measures(matching(y))
8-element Array{NamedTuple{(:name, :target_scitype, :supports_weights, :prediction_type, :orientation, :reports_each_observation, :aggregation, :is_feature_dependent, :docstring, :distribution_type),T} where T<:Tuple,1}:
(name = l1, ...)
(name = l2, ...)
(name = mae, ...)
(name = mape, ...)
(name = rms, ...)
(name = rmsl, ...)
(name = rmslp1, ...)
(name = rmsp, ...)
看看第一个
info(l1) # 注意, 在模型搜索中用的是info("model_name"),字符串,在指标搜索中用的是指标本身
julia> info(l1)
absolute deviations; aliases: `l1`.
(name = "l1",
target_scitype = Union{AbstractArray{Continuous,1}, AbstractArray{Count,1}},
supports_weights = true,
prediction_type = :deterministic,
orientation = :loss,
reports_each_observation = true,
aggregation = MLJBase.Mean(),
is_feature_dependent = false,
docstring = "absolute deviations; aliases: `l1`.",
distribution_type = missing,)